lymphocytic colitis in cats
Lymphocytic cells or certain types of white blood cells become misshapen and cancerous and speed the progress of the disease. Bile duct hypertrophy and fibrosis are present.
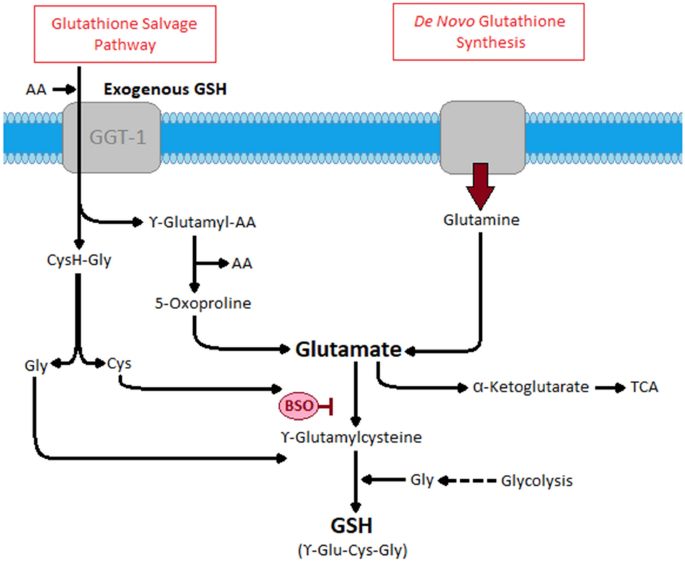
Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis In Cats With Naturally Occurring Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Alimentary Small Cell Lymphoma Scientific Reports
Lymphocytic-plasmacytic colitis is the most common form of colitis in both the dog and cat.

. Along with the debilitating effects of passing frequent loose stool called diarrhea many dogs. Colitis can be acute beginning suddenly and ending relatively quickly. Weight loss especially in cats dehydration especially if the diarrhea is very watery and lethargy are commonly associated with colitis as well.
It is thought to be caused by an abnormal immune response to environmental stimuli due to loss of normal immune regulation. The liver and spleen are usually the first organs affected. Idiopathic - perhaps immune-mediated response to antigens such as bacteria or diet eg lymphocytic-plasmacytic colitis.
However lymphocytic cholangitis does not progress to biliary cirrhosis. Stress Intestinal parasites such as roundworms Coccidia or Giardia Viral infections particularly feline leukemia virus FeLV feline immunodeficiency virus FIV or feline infectious peritonitis FIP A secondary reaction to antibiotics and other medications Pancreatitis. Lymphocytic plasmacytic enteritis is seen in both dogs and cats and is seen in all ages.
There may be an association between colitis in dogs and perianal fistulas especially in the German shepherd dog whereas purebred cats are affected more often than non-purebred cats. Lymphocytic-plasmacytic colitis was diagnosed in 6 cats. Bacterial - proposed on basis of response to antibiotics eg pathogens - Salmonella spp Salmonella spp and Campylobacter spp Campylobacter jejuni or commensal spp.
Inflammatory changes in the colon are usually lymphocytic-plasmacytic but other forms include eosinophilic neutrophilic and granulomatous enteritis. Colitis is an inflammation of the colon also known as the large intestine. Lymphocytic-plasmacytic gastroenteritis is an inflammatory bowel disease in which lymphocytes and plasma cells antibodies enter the lining of the stomach and intestines.
Lymphocytic cholangitis is a slowly progressive chronic disease characterised by infiltration of the portal areas of the liver with inflammatory cells mostly lymphocytes and plasma cells. While producing little or no stool is another common sign. Lymphocytic plasmacytic enteritis is seen in both dogs and cats and is seen in all ages.
It is most common in middle aged and older animal. Owners sought veterinary care because of semiformed -to-liquid feces tenesmus fresh blood andor mucus in the feces or increased frequency of defecation in their cats. Lymphocyticplasmacytic colitis was diagnosed in 14 cats during a 5-year period.
Signs of colitis include blood andor mucus in the stool diarrhea and frequent defecation of small amounts of feces. Bacteria in the intestine may also be a trigger. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association 184 9 1133-1135.
Colitis can be chronic constant acute come on suddenly or chronically episodic meaning that it comes and goes. Elevated lymphocytes in cats can be caused by two specific types of leukemia known as chronic lymphocytic leukemia CLL and acute lymphoblastic leukemia ALL. Lymphocytic plasmacytic infiltration in the colonic lamina propria was found on colon biopsies.
What to Watch For Diarrhea Vomiting Anorexia. Common sites of lymphoma in cats include. These dogs and cats with colitis are very uncomfortable and often their appetite is suppressed due to a general state of ill health.
The signs and symptoms can vary in intensity and frequency but generally cats exhibit signs of disease intermittently at first with the frequency of episodes increasing over time. Lymphocytic-plasmacytic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Be on the lookout for several of these common colitis symptoms in various combinations.
Other physical symptoms of. In one study cats were initially treated with dietary fiber or with dietary fiber and pharmacologic intervention prednisone tylosin or. Or chronic lasting for weeks and recurring periodically.
Although some patients with LPE may have no clinical signs some may have life threatening manifestations. The inflammation can be confined to the colon or also involve the small intestine and then is often termed as. This term describes lymphoma that affects the gastrointestinal tract.
Watery or bloody diarrhoea. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is currently more treatable than acute lymphoblastic leukemia 1 2 but both are life threatening. Lymphocytic leukemia in short and simple terms is a cancer that starts in the bone marrow and quickly spreads to other areas of the body.
Other infectious causes include. Lymphocytic colitis is a condition that affects your large intestine. Signs vary greatly in type severity and frequency.
There are several potential causes of colitis. The symptoms of colitis in cats. Lymphocytic colitis is form of microscopic colitis a condition that is characterized by inflammation of the colon large intestines.
Lymphocytic leukemia in short and simple terms is a cancer that starts in the bone marrow and quickly spreads to other areas of the body. The calling card of colitis in cats is a loose or mostly wet stool containing mucus and sometimes blood. While most cats with lymphocytic plasmacytic gastroenteritis are middle-aged this disease has been diagnosed in cats as young as 5 months.
Cats with lymphocytic-plasmacytic colitis may respond to dietary management alone eg lamb and rice horsemeat or a commercially available diet. This is by far the most common type of lymphoma in cats accounting for 50-70 of feline lymphoma cases. Cats with lymphocytic-plasmacytic colitis may respond to dietary management alone eg lamb and rice horsemeat or a commercially available diet.
Lymphocytic-plasmacytic colitis in the cat. Mucous or jelly in the stools. It is most common in senior cats with the average age at diagnosis ranging from 9-13 years old.
Lymphocytic-plasmacytic colitis in the cat.

What Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease In Cats Canna Pet

Feline Colitis An Infection In The Colon

Feline Chronic Enteropathy Marsilio 2021 Journal Of Small Animal Practice Wiley Online Library

Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ibd One Health Institute

Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology In Warthin S Tumor A Diagnostic Tool Tumor Diagnostic Tool Needle

Inflammatory Bowel Disease Ibd In Cats Halifax Vet Centre

Histology Of Intestinal Mucosa Of Dogs With Ibd After Treatment With Download Scientific Diagram

Feline Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treating Ibd In Cats
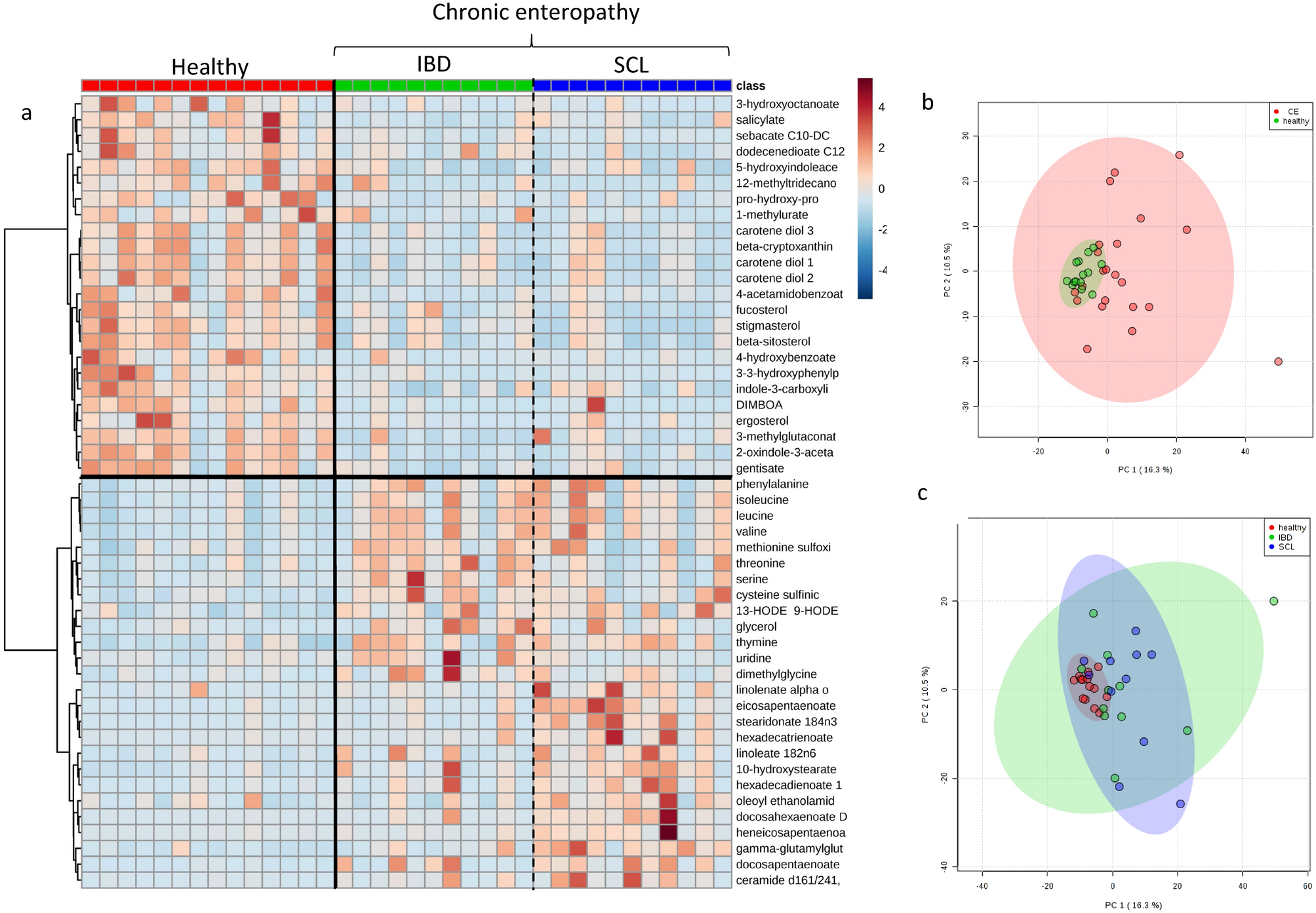
Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis In Cats With Naturally Occurring Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Alimentary Small Cell Lymphoma Scientific Reports

Inflammatory Bowel Disease In Cats Natural Treatment
Colitis In Cats What It Is Symptoms Causes Treatment

Colitis In Cats What It Is Symptoms Causes Treatment

Celiac Disease Colitis Microscopic Colitis Celiac Disease

Histopathologic Phenotypic And Molecular Criteria To Discriminate Low Grade Intestinal T Cell Lymphoma In Cats From Lymphoplasmacytic Enteritis Freiche 2021 Journal Of Veterinary Internal Medicine Wiley Online Library
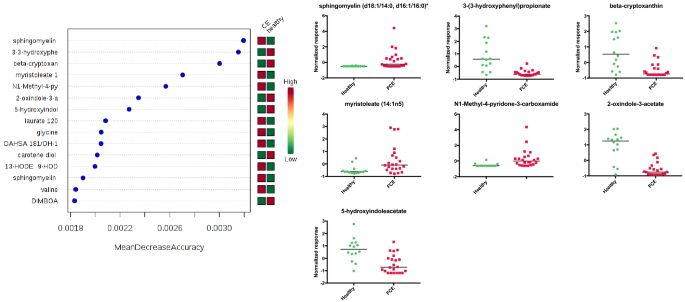
Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis In Cats With Naturally Occurring Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Alimentary Small Cell Lymphoma Scientific Reports

The Role Of The Microbiota In Feline Inflammatory Bowel Disease Abstract Europe Pmc

Histopathologic Phenotypic And Molecular Criteria To Discriminate Low Grade Intestinal T Cell Lymphoma In Cats From Lymphoplasmacytic Enteritis Freiche 2021 Journal Of Veterinary Internal Medicine Wiley Online Library

Pdf Inflammatory Bowel Disease In Veterinary Medicine
Lymphocytic Plasmacytic Gastroenteritis In Cats Vca Animal Hospital